On 1 February 2024, France’s Director General of Armaments (DGA) made notification of acquisitions by the French military in 2023, detailing a vast array of expenses, amounting to €20.3bn ($21.8bn), drawn from funds allocated by the Military Programming Law (MPL) 2024-2030, passed in July 2023.
Some €9bn, was allocated in December alone.
The full MPL 2024-2030 spending plan represents a historic commitment to defence spending for the period, with the total for the next seven years expected to be €413.3bn.
Starting from the 2023 budget of €43.9bn, the MPL stipulates an increase of €3.3bn to the defence budget in each of 2024 and 2025. The increases then slow to a €3.2bn raise each year from 2026 to 2028, and then accelerate by an additional €3.5bn every year afterwards until 2030.
The annual defence budget will reach a height of €67.4bn by the end of the programme.
GlobalData defence analyst Tristan Sauer commented on this development, stating, “The sustained escalation of French defence spending and acquisitions in 2023 is a testament to the Military Planning Law’s effective approach to defence budgeting. The current spending under the 2024-2030 MPL builds upon the foundation laid by the 2019-2025 MPL, furthering France’s strategic modernisation objectives.”
“The imperatives driving this modernisation have intensified recently,” Sauer continued. “France’s focus on ramping up defence industrial capacity is deemed essential in preparing for potential high-intensity conflicts, as outlined in the 2023 Strategic Plan. With key programs such as Scorpion and Caesar, initiated under the previous MPL, scaling up production, it’s expected that more funding will be directed towards these successful endeavours.”
This injection of funds is a strategic move underlining France’s doctrine of strategic autonomy. It reinforces its position as a significant actor in European defence, being the sole nuclear power that is a member of both the European Union and Nato.
The 2023 acquisitions for France include a range of new equipment for the Army, encompassing Caesar cannons and Serval Armoured Vehicles, as well as Caiman helicopter transports for the Special Forces. These acquisitions are instrumental in fortifying France’s military capabilities, ensuring it remains well-equipped to confront contemporary defence challenges effectively.
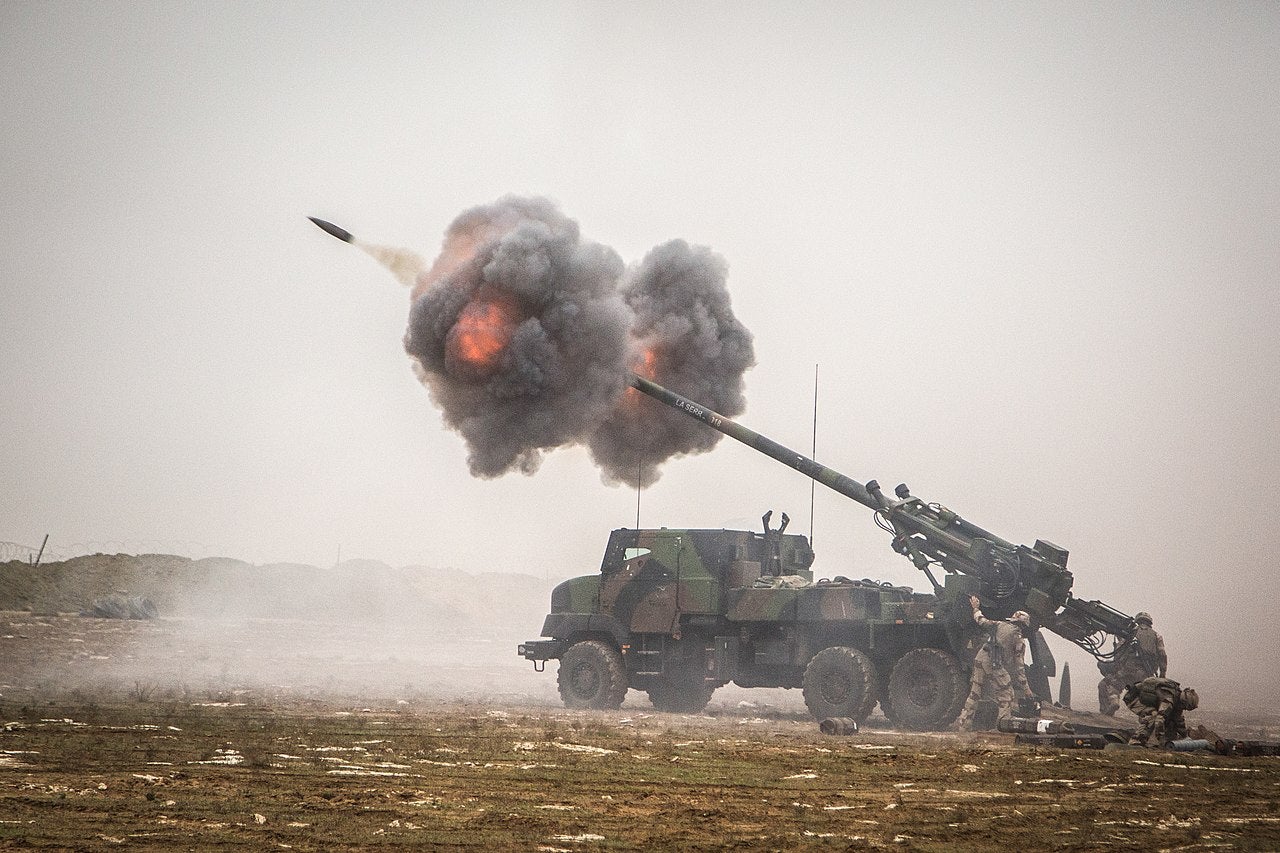
109 Next-Generation Caesar Cannons:
The order for 109 next-generation Caesar cannons marks a significant upgrade for the French ground forces. Finalised on December 30, 2023 by the DGA, this deal with Nexter Systems represents a strategic investment of approximately €350m. The Caesar Mk II systems, an advancement over the current models, bring a host of improvements focusing on mobility, connectivity, ballistic protection, and firing efficiency.
These enhancements are set to substantially boost the artillery capabilities of the French forces. The Caesar, a system that has been operational since 2008, is noted for its effective combat performance, striking a balance between a towed cannon and an armoured self-propelled gun. Mounted on a 6X6 truck with an armoured cabin, it offers a firing range exceeding 40km, and on the move it can achieve road speeds over 80km/h, with an un-refuelled range beyond 600km. Its mobility and precision provide an asset in long-range fire support.
Transportable as a single load by a C-130 Hercules transporter, the Mk II version retains the airmobile feature of the current Caesar while introducing significant upgrades. It includes a cabin with enhanced armour for better protection against improvised explosive devices, mines, small arms fire, and artillery fragments. Moreover, the Mk II will have a more powerful engine, a new automatic transmission, and an updated chassis. These improvements not only augment the cannon’s mobility but also its tactical versatility.
In terms of firepower, the Caesar Mk II’s artillery precision will be further refined through the integration of state-of-the-art fire control software. It remains compatible with current ammunition types while being prepared for future precision munitions. The vehicle will also incorporate common vehicle electronics used in modern and interconnected SCORPION program equipment, enhancing its operational efficiency and integration with other systems.
420 Serval Armoured Vehicles:
On December 30, 2023, the DGA placed an order with KNDS France and Texelis for 420 Serval light multi-role armoured vehicles. Valued at nearly €500m, this order is a continuation of the SCORPION program, following an earlier acquisition of 364 Serval vehicles.
The Serval is a 4×4 armoured vehicle weighing between 15 to 17 tons depending on its load, embodies the integration of modern battlefield technologies. It features a remotely operated turret, threat detection sensors, and the SCORPION Combat Information System (SICS), allowing real-time tactical data sharing with other engaged SCORPION program vehicles. The vehicle can transport up to eight fully equipped soldiers in addition to its two-member crew, providing an additional tactical mission for troop mobility.
Designed to be agile and versatile, the Serval is part of a broader initiative to renew the army’s combat vehicles, joining the Griffon and Jaguar, armoured vehicles that are also being developed under the SCORPION program. The Serval is specifically aimed at replacing the aging Véhicule de l’Avant Blindé (VAB), which has been in service for over four decades.
This new batch of vehicles will include the development and production of an Electronic Warfare (EW) version, in addition to the already planned variants like the armoured patrol vehicle, target acquisition surveillance vehicle, intelligence reconnaissance vehicle, and tactical communication node vehicle. This diversification is inline with the Serval’s requirement to adapt to varied combat scenarios.
Production of these vehicles is set to take place at Roanne in the factory of KNDS France, which also manufactures the Griffon and Jaguar vehicles. The opening of this new production line has already generated over 1,000 jobs, illustrating an economic benefit to this defence procurement. Additional industrial sites across France, including Texelis in Limoges, Safran Electronics & Defense in Montluçon, and others in regions like Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes, Centre-Val de Loire, and Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur, are also benefit from this order, according to a release from the French Ministry of Defence on 1 February, 2024.
The Serval is a 4×4 armoured vehicle weighing between 15 to 17 tonnes depending on its load, embodies the integration of modern battlefield technologies. It features a remotely operated turret, threat detection sensors, and the SCORPION Combat Information System (SICS), allowing real-time tactical data sharing with other engaged SCORPION program vehicles. The vehicle can transport up to eight fully equipped soldiers in addition to its two-member crew, providing an additional tactical mission for troop mobility.
Testing and qualification of the Serval prototypes has included trials in various terrain conditions, accelerated aging tests to simulate years of use, mine explosion resistance tests, and compatibility checks with the A400M transport aircraft.
The inclusion of the Serval in the French Army’s fleet by 2030, with a total of 978 vehicles, will be an enhancement to the army’s operational readiness and capability for high-intensity combat scenarios.
Eight NH90 Caiman Helicopters for Special Forces:
The acquisition of eight additional NH90 Caiman helicopters for the French Special Forces, as announced by the DGA on December 20, 2023, will enhance French aero-combat and tactical transport capabilities for special operations. This order, valued at €305m, supplements ten helicopters previously ordered, bringing the total count to 18 NH90 Caiman helicopters expected by 2030.
The NH90 is an 11-tonne class twin-engine helicopter, a product of European cooperation involving France, Italy, Germany, the Netherlands, and Belgium. It is developed by the NHIndustries consortium, comprising Airbus Helicopters, Leonardo, and Fokker. The NH90 program, managed for France by the DGA, relies on the Nato Helicopter Management Agency (NAHEMA) for overall program management.
The NH90 Caiman, in its special forces configuration, “Standard 2″, is under development to meet the demanding requirements of special operations, providing new intervention capabilities in environments with reduced visibility.
Among the primary upgrades in the “standard 2” version are advanced mission equipment, including a mission infrared camera with a laser pointer and designator (EOS410 from Safran), integration of new armaments, and a specialised radio communication kit for conducting joint and coalition operations. These enhancements are meant to boost the NH90’s capability for commando insertion and extraction, fire support, and tactical communications.
The NH90 Caiman helicopters will be manufactured at the Airbus Helicopters France site in Marignane, Bouches-du-Rhône. Post-production, they expected to be delivered to the 4th Special Forces Helicopter Regiment (4e RHFS) in Pau over the period 2026-2029, and will replace the older CARACAL and COUGAR models.