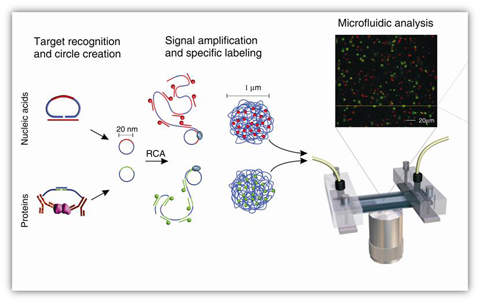
Q-linea is a developer of instruments and systems for nucleic acid and protein analysis based in Sweden. Combining a set of innovative molecular biology tools with high-performing readout technology, Q-linea can provide biological warfare agent detection and identification capabilities with unprecedented performance.
Genetic and immunological detection platform
Using unique molecular procedures, termed padlock probes and proximity ligation, Q-linea’s amplified single-molecule detection platform can be used for both genetic and immunological detection. This allows the full spectrum of biological threats, including bacteria, spores, viruses and toxins, to be analysed using a single instrument.
The amplified single-molecule detection platform features high specificity, a detection limit of hundreds or less of bacterial genomes or spores per sample, and the capability of detecting multiple agents in a single analysis.
Biowarfare agent detection system
The amplified single molecule detection technology is implemented in the Aquila instrument platform. The platform is modular, offering the flexibility to tailor the system to specific customer needs. For example, the instrument may be connected to an air sampler and integrated into a stand-alone biodetection system to continuously and autonomously monitor for biowarfare agents or other hazardous biological material. In this configuration, the instrument is equipped with a sample preparation and sample processing unit capable of accepting samples continuously with an interval of a few minutes.
Field laboratory platforms
In another configuration, the Aquila platform may be set up to analyse batches of prepared samples, suitable for a field laboratory setting. In both cases, assay times can be between 30 minutes and one hour, depending on requirements.
Molecular diagnostic technologies
In contrast to many other molecular diagnostic technologies, Q-linea’s amplified single-molecule detection system uses a single end-point measurement. This means that each sample occupies the detection unit for a short time only. Therefore, the footprint of the instrument can be kept small while allowing a high sample throughput. In addition, this means that the system can accept incoming samples at regular or irregular intervals, without the need to stack up samples on hold and run them in batch as would be the case for a micro titer plate-based instrument, as is commonly used in quantitative PCR or ELISA assays.