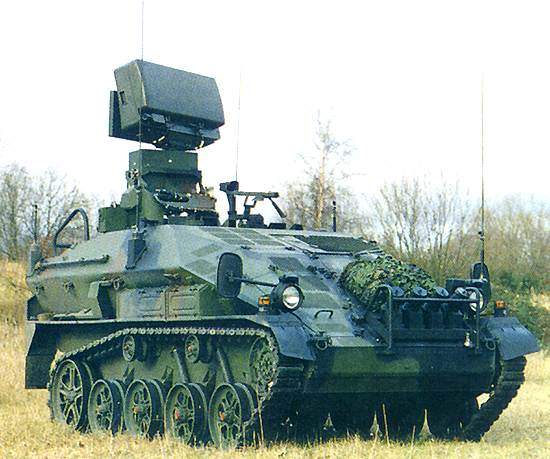
The ASRAD-R export version of the LeFlaSys SHORAD missile system.
The LeFlaSys light mechanised SHORAD (short-range air defence system) has been developed for the German Army by STN ATLAS Elektronik GmbH (now Rheinmetall Defence Electronics) in Bremen and Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) in Kassel, Germany.
The export version is known as ASRAD (atlas short-range air defence system). It is based on the Wiesel 2 carrier vehicle, which was developed by Rheinmetall Landsysteme (formerly MaK).
The system provides protection for vital assets such as command, control communications and information centres (C3I centres), airfields and troops on the move, or in the battlefield against the threat of low-level flying fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft.
LeFlaSys air-defence missile system
An army platoon would be equipped with a LeFlaSys air defence platoon command post and typically between five and eight Ozelot air defence weapon platforms. The LeFlaSys system is expected to fulfil the short-range air defence requirements of the rapid reaction forces of the German Army. Series production of 50 weapon platforms, ten platoon command post vehicles and seven AFF battery command vehicles began in 2000. The German Army received its first platoon of the LeFlaSys air defence system in June 2001 and deliveries were completed by the end of 2004.
The Hellenic Army of Greece placed an order for 54 ASRAD systems armed with Stinger missiles in October 2000. The first was delivered in October 2004. Deliveries completed in 2006. The systems are mounted on HMMWV vehicles, modified by ELBO/AMG of Greece.
ASRAD-R SHORAD missile system
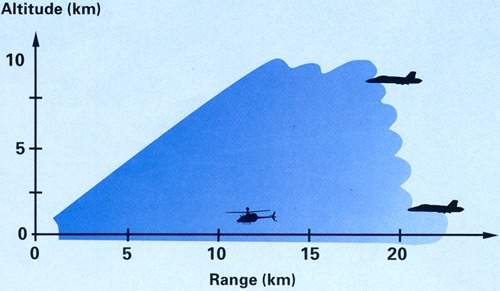
Rheinmetall Defence Electronics, in conjunction with Saab Bofors Dynamics, have developed ASRAD-R which is based on the Saab Bofors Bolide missile and the Saab (formerly Ericsson) Microwave Systems HARD 3D search radar. The Bolide laser-guided surface-to-air missile has been developed from the RBS 70 and has a maximum range of 8km and altitude coverage of up to 5,000m.
In August 2002, Finland placed the first order for 16 ASRAD-R systems, which are mounted on containers transported by Mercedes-Benz UNIMOG 5000 vehicles. First deliveries were in 2004 and were completed in June 2008.
In February 2007, Rheinmetall and Saab Bofors announced the development of a navalised version of ASRAD-R. The naval variant has four Bolide missiles mounted on a pedestal with sensors including infrared, CCD TV and eyesafe laser rangefinder.
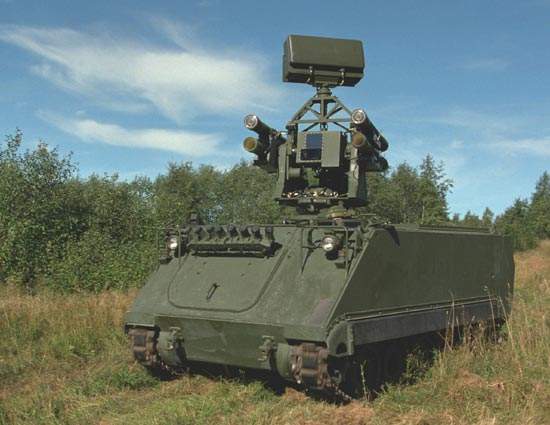
Ozelot surface-to-air weapon system
The Ozelot weapon system is built on the Wiesel 2 small armoured tracked vehicle. The Ozelot carries four ready-to-fire Stinger surface-to-air missiles but can also be armed with Igla, Mistral, RBS 70 mk2 or Starburst missiles.
Ozelot is air transportable in a CH-53 helicopter.
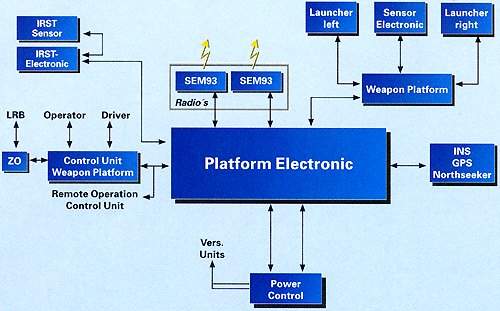
The main components of the weapon platform are: pedestal with azimuth and elevation; drive and combined sensor and system electronics including the missile interface; electronics; multipurpose launcher; pedestal electronics systems; control and display unit.
Fire control
The HARD 3D search and acquisition radar is installed on the platoon command post. HARD, supplied by Saab (formerly Ericsson) Microwave Systems, operates in the X band and has a range 20km. HARD has a MTI (moving target indicator) mode for fixed-wing targets, helicopter mode for helicopter detection and analysis and a non-MTI mode for increased sensitivity and detection of tangential targets. Data processing allows automatic track initiation on both targets and jammers. The radar uses a complex search beam pattern with multiple tracking beams in the target direction.
Target acquisition is achieved, either by the HARD radar, which downloads target data via radio data link to the Ozelot weapon platform, or by the Thales (formerly Pilkington) Optronics ADAD passive infrared search and track system (IRST), mounted on the forward part of the roof.
For target tracking, the Ozelot is equipped with its own stabilised forward-looking infrared (FLIR) sensor, TV and laser rangefinder as well as dual mode autotracking. The system is capable of automatic range and envelope determination and fire control and second shot capability on the same approaching target. Remote control at up to 100m is possible using the same control and display unit.
In addition to the weapon pedestal, there is a navigation system with a global positioning system (GPS), inertial navigation system and north-finding gyroscope, and the C31 interface via VHF-radio for data and voice transmission.
Platoon command post
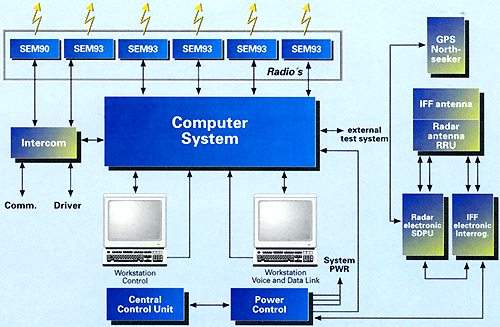
The purpose of the platoon command post is to carry out target acquisition for between five and eight LeFlaSys Ozelot weapon platforms at a range of approximately 20km. Target data is transmitted via a radio data link to the weapon platforms in the platoon and also to other platoons. Evaluation of target data received from other sensors including allied forces, threat analysis and identification friend or foe (IFF) is carried out in the platoon command post.
The platoon command post vehicle is equipped with a Saab HARD 3D X-band radar for target acquisition and for tracking in track-while-scan mode.
The range of the radar is 20km. The radar uses Kalman filtering and moving target indication (MTI). The IFF MSR 200 XE identification friend or foe (IFF) is integrated into the radar system.
The platoon command post is also based on the Wiesel 2 vehicle. The platoon leader’s station and the radar operator’s station are equipped with control and display units with flat panel displays for air picture data and command and control data. The command post uses advanced 64-bit computer technology for C3 air picture data processing, threat analysis and built-in test.
Communication links are based on VHF radios, SEM 93 and SEM 80/90 supplied by Alcatel SEL AG of Stuttgart, for voice and data transmission.
The system’s navigation suite includes a Rockwell Collins PLGR AN-PSN11 global positioning system and a Talin navigation system from Honeywell.