Located north-west of Lashkar Gah in the Helmand province, Camp Bastion is a prominent UK military base in Afghanistan. The base is developed in a distant desert area. It is currently serving as the fifth busiest UK-operated airport and is the largest overseas military base camp installed by the UK since World War II.
Camp Bastion is operated by HM Armed Forces, and categorised into two divisions, namely Bastion 1 and Bastion 2. Camp Barber (US) and Camp Viking (UK) are the two tenant camps located in Bastion 1. Two more camps Camp Leatherneck (US) and the Afghan National Army (ANA) Camp Shorabak are situated adjacent to the Bastion camp. Approximately £50m has been spent on the construction of Camp Bastion, two adjacent bases and an airfield.
G-3 Systems built the medical treatment facility (MTF) at Camp Bastion in Southern Afghanistan with a minimum life expectancy of three years. The MTF is currently being operated by Joint Forces Medical Group.
Camp Bastion airfield history
Che Camp Bastion airfield was built in April 2006 by two Royal Air Force (RAF) air traffic control unit members. It was built on a gravel dirt track on which the first aircraft landed 90min upon completion of the runway construction.
The base was initially designed to manage less than three aircraft movements a week. It has become one of the busiest UK-operated airports and currently handles 600 aircraft a day (18,000 a month), which is more traffic than Luton, Edinburgh or Birmingham, Leeds-Bradford and Coventry Airports.
The base is a hub for conducting combat, medical evacuations and logistics sustainment flight operations.
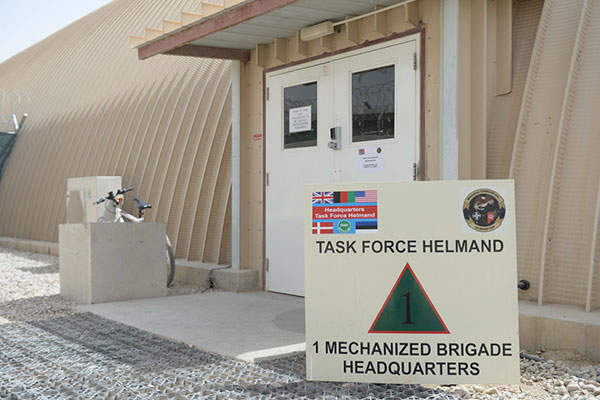
The headquarters of Task Force Helmand was relocated from Lashkar Gah to the UK’s main base at Camp Bastion in August 2013. A battle school was launched at the base in October 2013, to provide training for the Afghan troops.
The Tongan troops were deployed to Helmand province in 2010 and their missions were ended in April 2014. Danish and Estonian soldiers completed operations at Camp Bastion in May 2014.The last UK military base and US Camp Leatherneck were handed over to the Afghan security forces in October 2014.
Garrison facilities
Camp Bastion can accommodate between 11,000 and 12,000 troops; 2,000 of which are residing adjacent to the base. The base is headquarters to HM Armed Forces and has several amenities for residing troops, including hangars, temporary portable aircraft arrestor equipment, oxygen and nitrogen production plants, and an environment-conditioning, design, installation and maintenance system.
In 2007, a water bottling plant was set up at the base. It has a capacity to process up to 15,000gal of water a day. Royal Engineers sunk borewells between 300ft and 400ft-deep and the plant was built at cost of £11m ($17.84). US contractor KBR employed 400 people from Nepal and Sri Lanka at the water plant.
A UK-operated field hospital (Role 3 hospital) built in 2006 was closed in September 2014. The trauma care facility was equipped with an operating theatre, an intensive care unit, radiographic equipment, X-ray machines and CT scanners. A new military trauma facility located at Camp Shorabak is now being operated by the ANA.
The central warehouse building at the base can store up to 27,000t of salad and fruit. The base also has eight incinerators for waste disposal.
Base protection
Radars installed in Camp Bastion provide surveillance and protection by detecting human or aircraft movements coming towards the base. The radars cover a distance of up to 20 miles. The soldiers at the base are trained to identify improvised explosive devices (IED).
Camp Bastion technology
An advanced technology incorporating the US Marine Corps (USMC) precision approach radar is deployed in the base. The radar guides aircraft to land on the runway safely during adverse weather conditions. The base is also equipped with a mobile visual control room.
Air traffic control facilities
Air traffic control equipment has been installed in the base to ensure the airfield operates effectively in all weather conditions.
A second mobile air traffic control (ATC) tower became operational at Camp Bastion in June 2011. RAF and US Marine Corps (USMC) are stationed at the new ATC tower. Host Systems supplied the first and second ATC systems for the base. Northrop Grumman Corporation provided radio communication system for air traffic control operations.
The base features a four-mile long and two-mile wide airstrip, which can handle C-17 and C-130 transport aircraft. The airstrip also accommodates Apache and Chinook helicopters deployed at the heliport. The largest aircraft, Antonov An-225, operated by Ukraine’s Antonov Airlines, touched down at the base in March 2011.
Camp Bastion has two runways. The first runway (01R/19L) was constructed by 39 Engineer Regiment in March 2007 for handling aircraft movements. It is surfaced with gravel. In May 2007, the construction of the second 2,350m-long and 28m-wide runway (01L/19R) began at the Task Force Helmand logistics hub, Camp Bastion.
The second runway, which became fully operational in December 2007, enabled the RAF’s C-17 GlobeMaster to land directly in the base rather than the Kandahar Airfield. The runway was extended to 3,500m and paved with concrete and asphalt under a $141m airfield expansion project. It was officially opened to traffic in February 2011. The old runway is now used as a parallel taxiway.
The air traffic controller squadron stationed at Camp Bastion endorses UK operations in Southern Afghanistan. They provide training to select US Marine Corps according to the UK’s air traffic control standards. The group of personnel working on either side of the tower control the aircraft landing on the ground.
The Global Military Rotorcraft Market 2011-2021
This project forms part of our recent analysis and forecasts of the global military rotorcraft market available from our business information platform Strategic Defence Intelligence. For more information click here or contact us: EMEA: +44 20 7936 6783; Americas: +1 415 439 4914; Asia Pacific: +61 2 9947 9709 or via email.