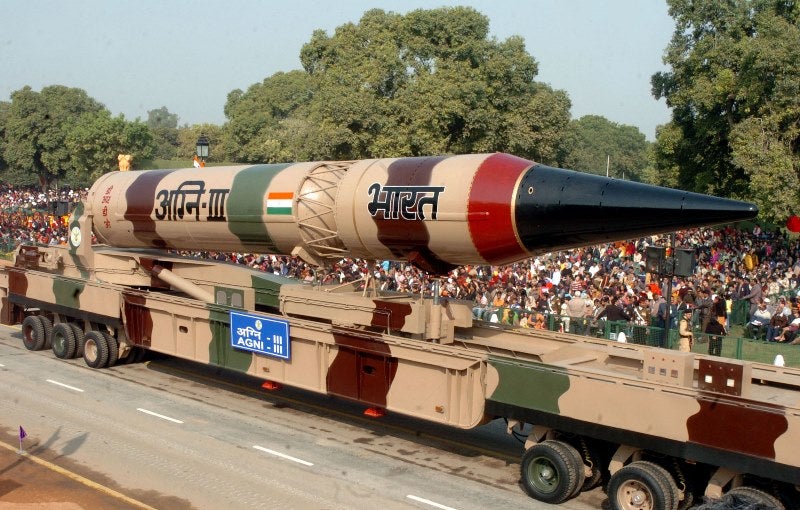
The Strategic Forces Command of the Indian Army has carried out the first night trial of the nuclear-capable Agni-III surface-to-surface ballistic missile at the Integrated Test Range (ITR) on APJ Abdul Kalam Island off the coast of Odisha state.
The trial was carried out from a mobile launcher at launch complex-4 of the ITR with logistic support from the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
According to the NDTV, defence sources said that the outcome of the trial is pending.
The intermediate-range missile has a strike range of more than 3,500km and the flight test is part of a user trial by the army, the report stated.
Agni-III missile with a length of 17m, a diameter of 2m and a launch weight of around 50t has been already inducted into the armed forces, the report stated.
The NDTV report quoted a DRDO source as saying: “It was the fourth user trial in the Agni-III series carried out to establish the repeatability of the missile’s performance. For the first time, the test was conducted during night time.”
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataPowered by a two-stage solid propellant system, the nuclear-capable Agni-III missile is capable of carrying a 1.5t warhead, which is protected by carbon all composite heat shield.
The missile is equipped with hybrid navigation, guidance and control systems, as well as an advanced on-board computer.
A DRDO scientist told NDTV that the electronic systems are designed to withstand higher vibration, thermal and acoustic effects.
Agni-III, the third in the Agni series of missiles, was first tested on 9 July 2006 from Wheeler Island off the coast of Odisha, but the launch reportedly failed. It was again tested from Wheeler Island on 12 April 2007, which was successful. On 7 May 2008, India again successfully test-fired the missile.
The missile’s circular error probable (CEP) is in the range of 40m, making Agni-III the most accurate strategic ballistic missile of its range class in the world.